Code Node
The code node runs a C# script against the current workflow context. Use it for glue logic, calling backend services, or complex data transformations.
Access the Context
The script runs with a single global named Context, which is a ContextObject. Read and write values using Get, Set, or the standard dictionary and list APIs. Return values from the script are ignored, so update Context to persist results.
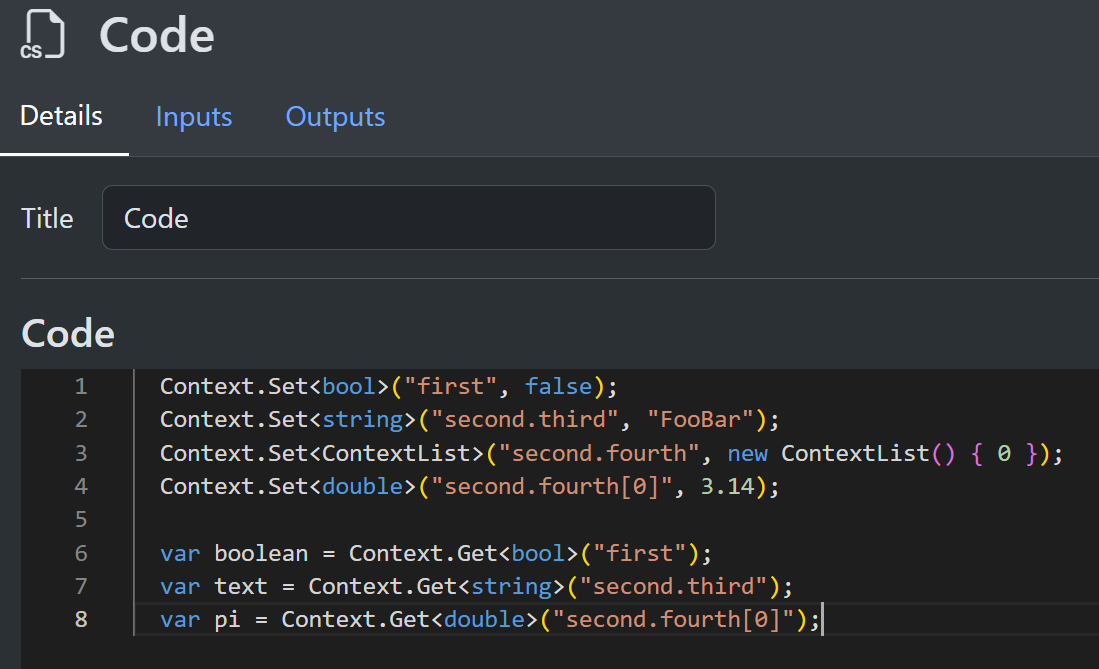
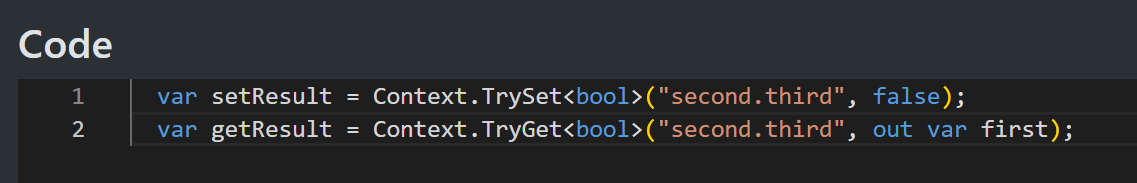
There are also TrySet and TryGet variations for scenarios where you do not know if they will succeed.
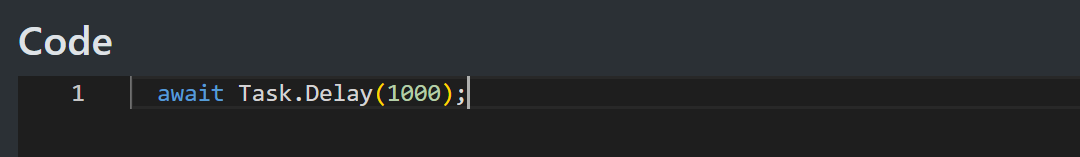
Asynchronous Code
You can perform await operations on asynchronous code in the usual way. It is recommended to use async operations when possible to free up the thread for slow operations. For example, file and network calls are typically quite slow and benefit from this approach.
 ```
```
Implicit Assemblies
The following using statements are implicitly already applied:
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using SharpOMatic.Engine.Contexts;
You can access the types defined in these namespaces.
Additional Assembly References
If you need to access assemblies or types not already implicitly added, you can do so easily. When adding the SharpOMatic engine in program setup, add the AddScriptOptions extension. The first parameter is a list of additional assemblies that should be made available. Note that the referenced assembly must be part of the owning project, so you might need to add it to your project references.
In the following example, we add the demo server assembly by specifying one of the types within it so the entire assembly can be found. The second parameter is the list of extra namespaces to add. Here we have the namespace of the demo server.
builder.Services.AddSharpOMaticEngine()
.AddScriptOptions([typeof(ClassExample).Assembly], ["SharpOMatic.DemoServer"])
Code compilation
Your code will automatically be checked to ensure it is valid. The familiar red error line will appear in the place the code has a problem. Do not ignore these because it indicates the code will fail at runtime. As noted above, you can add access to additional assemblies and types if you want to access backend-specific code.
Custom types and JsonConverter
The context must be serializable to and from JSON so that it can be saved to the database. This restriction allows a workflow to be suspended and restarted and allows intermediate states to be recorded to help with debugging.
Scalar values persist automatically with standard JSON serialization. Classes require a converter. You can register additional types from your project so they can be added to the context and persisted. Here is a trivial class definition.
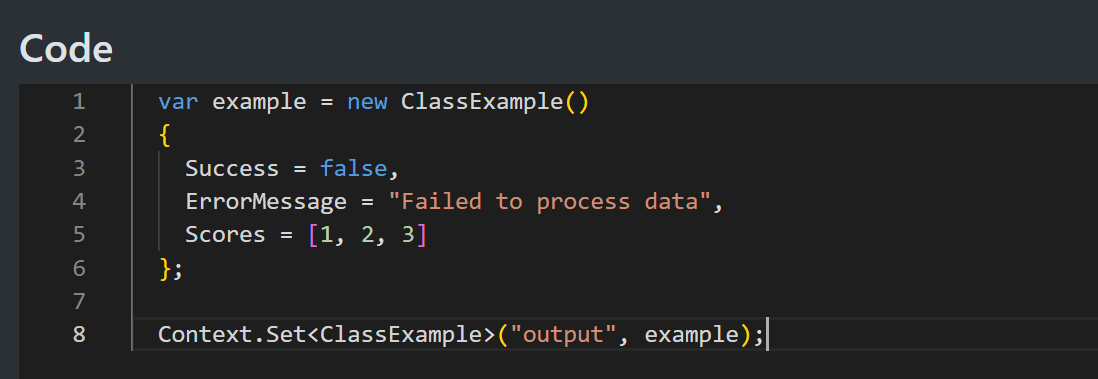
public class ClassExample
{
public required bool Success { get; set; }
public required string ErrorMessage { get; set; }
public required int[] Scores { get; set; }
}
Now you need to implement a JsonConverter for it.
public sealed class ClassExampleConverter : JsonConverter<ClassExample>
{
public override ClassExample? Read(ref Utf8JsonReader reader,
Type typeToConvert,
JsonSerializerOptions options)
=> JsonSerializer.Deserialize<ClassExample>(ref reader, Clean(options));
public override void Write(Utf8JsonWriter writer,
ClassExample value,
JsonSerializerOptions options)
=> JsonSerializer.Serialize(writer, value, Clean(options));
private JsonSerializerOptions Clean(JsonSerializerOptions options)
{
var inner = new JsonSerializerOptions(options);
inner.Converters.Remove(this);
return inner;
}
}
Provide the implementation type in the SharpOMatic setup and ensure the assembly and namespace are available to code execution.
builder.Services.AddSharpOMaticEngine()
.AddJsonConverters(typeof(ClassExampleConverter))
.AddScriptOptions([typeof(ClassExample).Assembly], ["SharpOMatic.DemoServer"])
Now we can access the class and add it to a context inside the Code node.