Handling Serialization
Context Serialization
The workflow context must be serializable to and from JSON so that it can be saved to the database. This restriction allows a workflow to be suspended and restarted and allows intermediate states to be recorded to help with debugging.
Scalar values
The following scalar values are internally registered and work automatically.
| Scalar values | Scalar values | Scalar values | Scalar values |
|---|---|---|---|
| bool | uint | char | TimeOnly |
| byte | long | string | Guid |
| sbyte | ulong | DateTime | Uri |
| short | float | DateTimeOffset | |
| ushort | double | TimeSpan | |
| int | decimal | DateOnly |
If you think a simple type has been missed, please raise an issue and it will be investigated and added.
Class instances
Classes always require a dedicated converter that derives from IJsonConverter.
The following built-in types already have converters.
- ContextObject
- ContextList
- AssetRef
- ChatMessage
To allow your own classes to be assigned to the context, you need to add a converter and then register it with SharpOMatic.
Custom converter
You can register additional types from your project so they can be added to the context and persisted.
Here is an example class definition.
public class ClassExample
{
public required bool Success { get; set; }
public required string ErrorMessage { get; set; }
public required int[] Scores { get; set; }
}
Now you need to implement an IJsonConverter for it.
public sealed class ClassExampleConverter : JsonConverter<ClassExample>
{
public override ClassExample? Read(ref Utf8JsonReader reader,
Type typeToConvert,
JsonSerializerOptions options)
=> JsonSerializer.Deserialize<ClassExample>(ref reader, Clean(options));
public override void Write(Utf8JsonWriter writer,
ClassExample value,
JsonSerializerOptions options)
=> JsonSerializer.Serialize(writer, value, Clean(options));
private JsonSerializerOptions Clean(JsonSerializerOptions options)
{
var inner = new JsonSerializerOptions(options);
inner.Converters.Remove(this);
return inner;
}
}
Provide the implementation type during SharpOMatic setup.
builder.Services.AddSharpOMaticEngine()
.AddJsonConverters(typeof(ClassExampleConverter))
For additional information about context, see the Context section.
Fast Deserialization
SharpOMatic has a custom JSON deserializer that is used to convert from a standard JSON string to a context-compatible data structure. This is used automatically whenever you specify a (json) input type to convert the supplied string into data that can be assigned to the workflow context.
Here you can see it being specified in the editor.
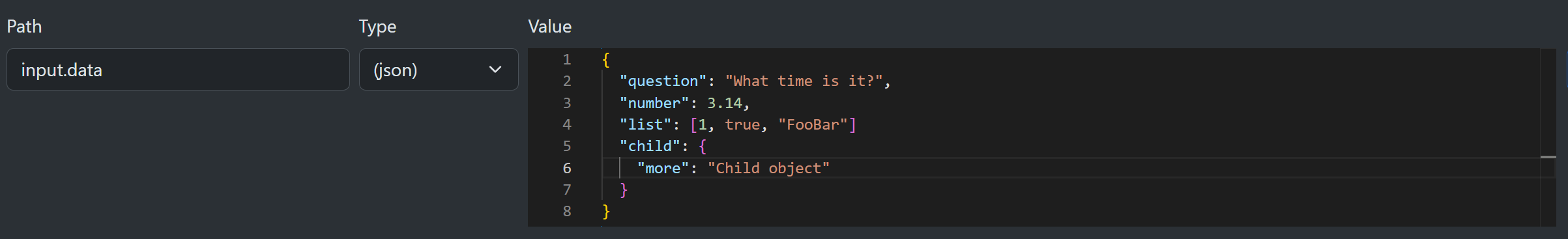
You can use the fast deserialization utility inside a Code node or your own code when constructing the inital context for a workflow invocation.
var json = """
{
"question": "What time is it?",
"number": 3.14,
"list": [1, true, "FooBar"],
"child": {
"more": "Child object"
}
}
""";
// Convert from JSON string to context-compatible data
var data = new FastJsonDeserializer(json).Deserialize();
// Put the data into the context
Context.Set("deserialized", data);
If we run this in a workflow, you can see that it was converted from a string to the default types for JSON data and placed into the context. This is really useful when you are importing blocks of JSON from external sources or data files.
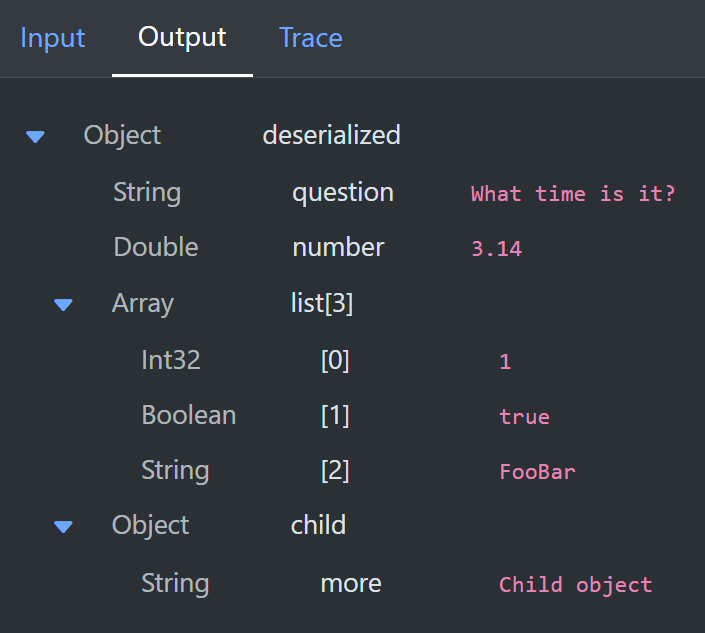
Numbers are converted to either int or double depending on whether they are whole numbers. Boolean and string values are converted to the matching C# type. Any object becomes a ContextObject and any array becomes a ContextList.